Making improper changes to the Registry can cause Windows to become unusable or unbootable. To prevent, restrict or block anyone from accessing Registry Editor in Windows 10, 8 and 7, you can disable Registry Editor using group policy, registry trick or third-party software.
Method 1: Disable Registry Editor Using Group Policy
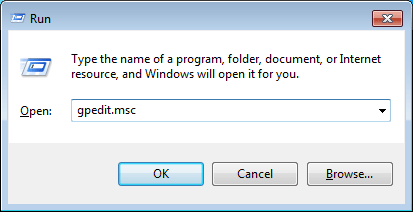
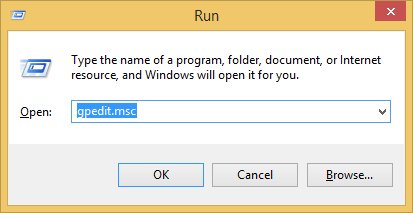
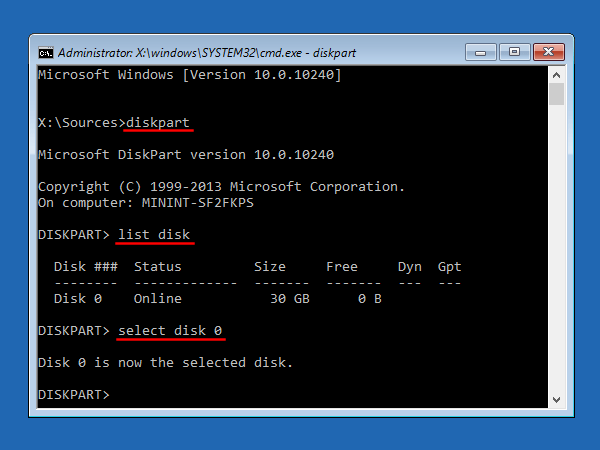
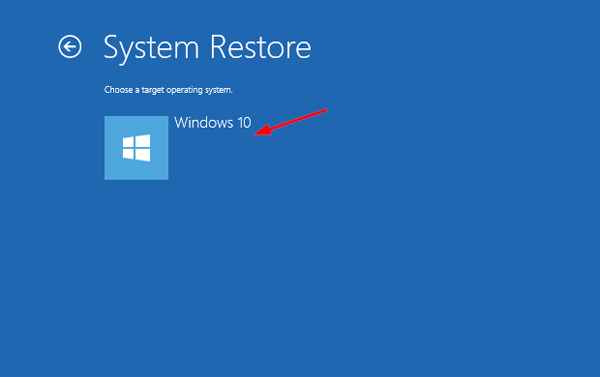
- Press the Windows key + R to bring up the Run box. Type gpedit.msc and press Enter.
![gpedit]()
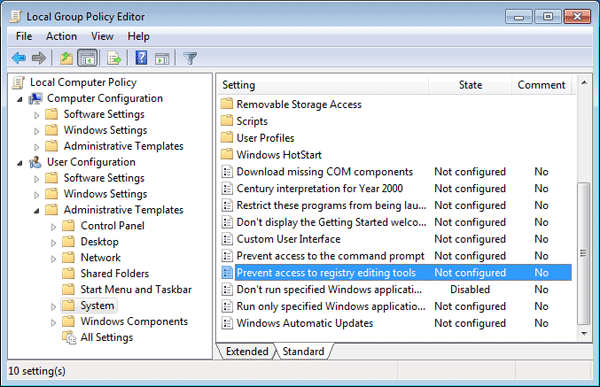
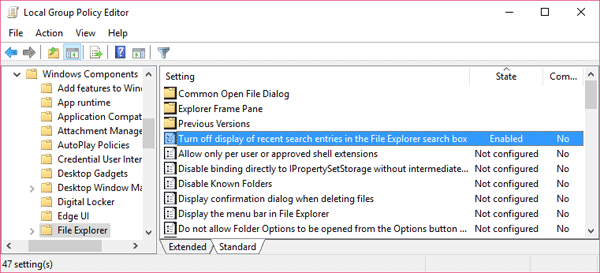
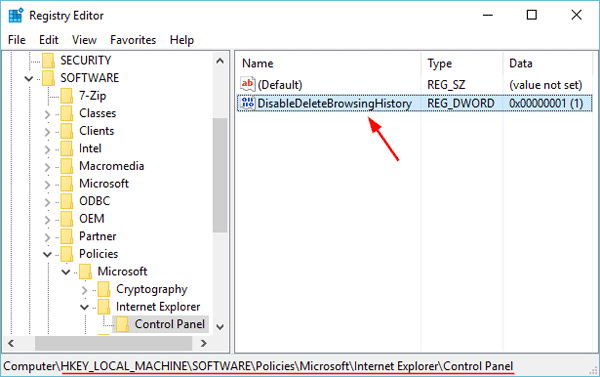
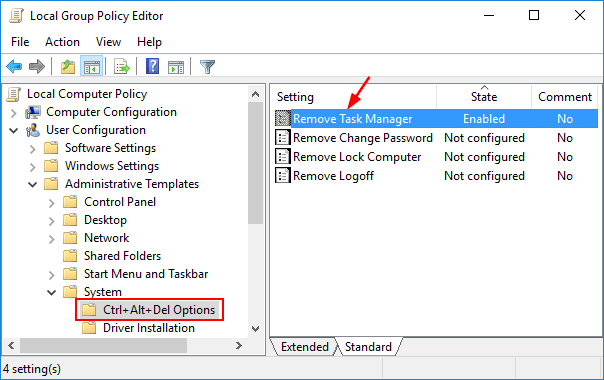
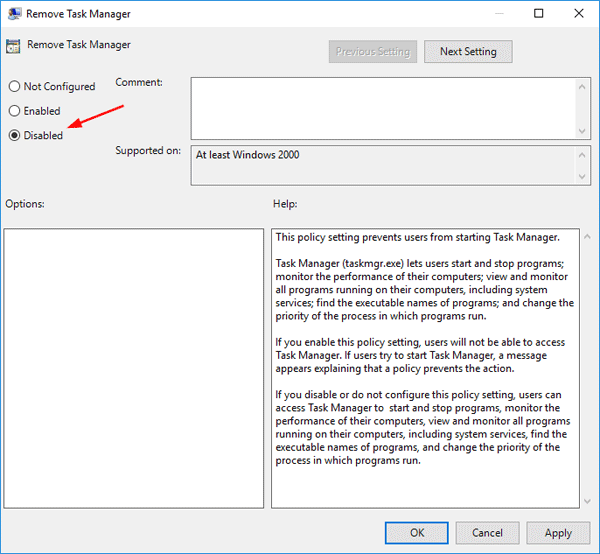
- When Group Policy Editor opens, navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > System. Double-click on Prevent access to registry editing tools on the right panel.
![prevent-access-to-regedit]()
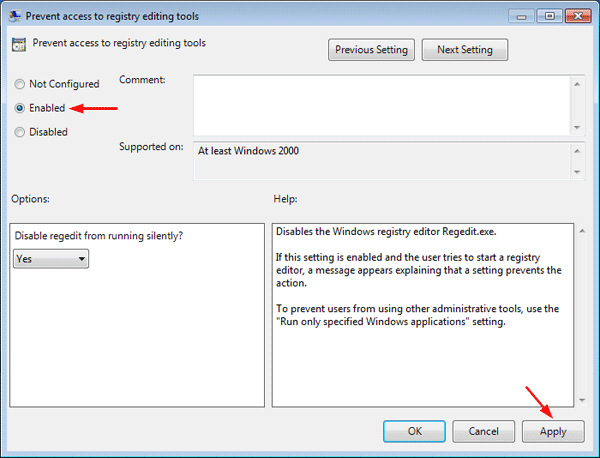
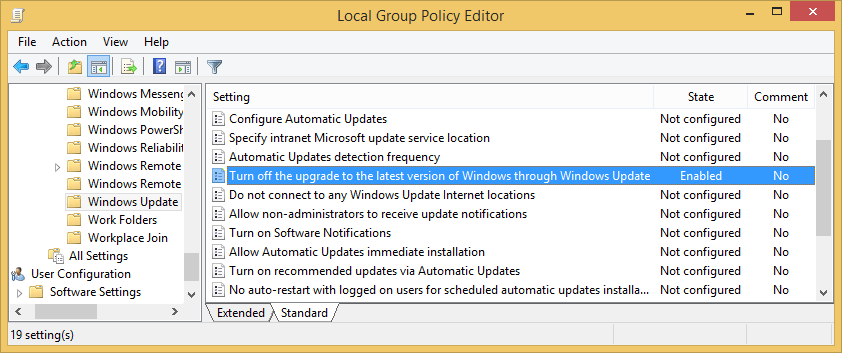
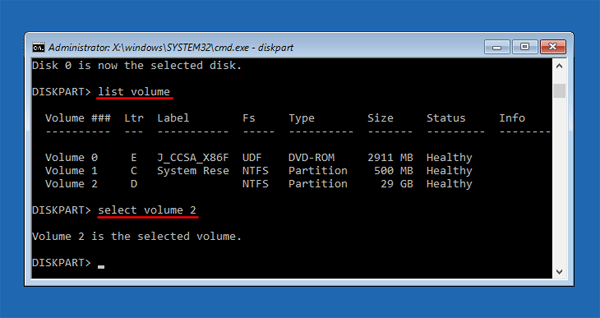
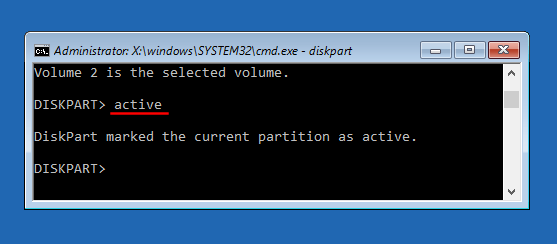
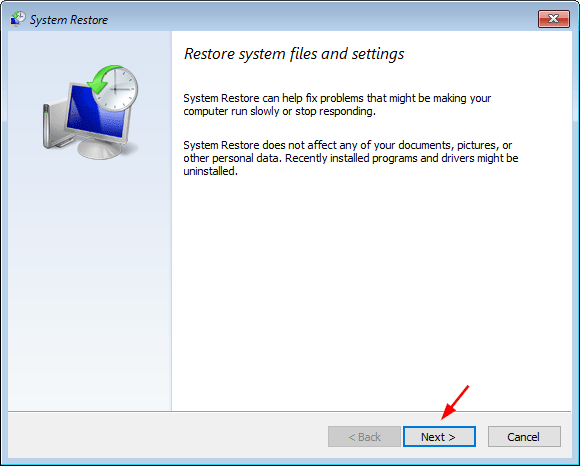
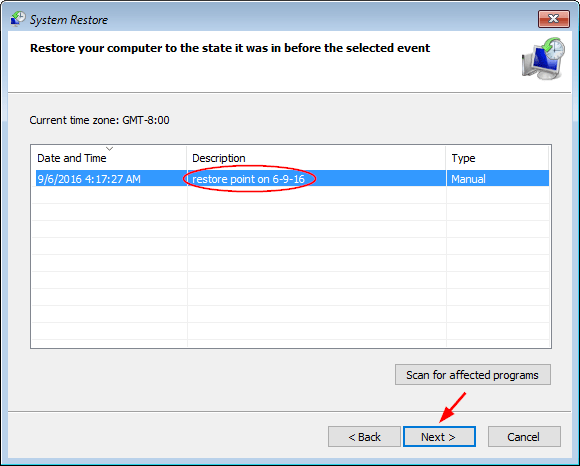
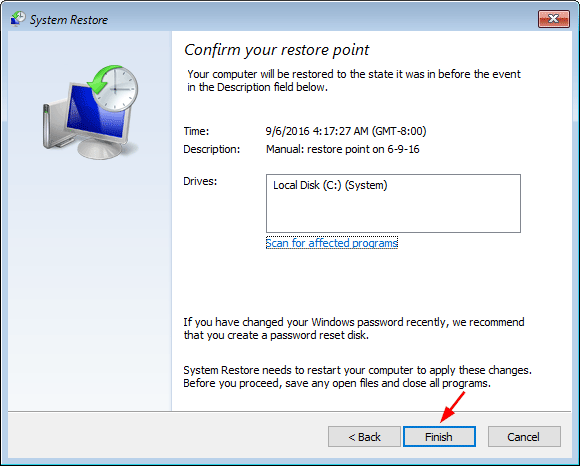
- Select the radio button next to Enabled, click Apply and then OK, then close out of Group Policy Editor and reboot your computer.
![prevent-access-registry-edit]()
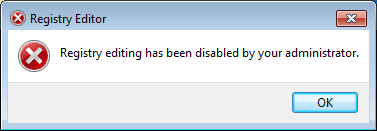
- When a user tries to access Registry Editor, they will get an error message saying “Registry editing has been disabled by your administrator“.
![registry-editing-disabled]()
This method will prevent all users from accessing Registry Editor, including yourself. To regain access to Registry Editor, you have to open Group Policy Editor again, and change the policy to Disabled or Not Configured.
Method 2: Disable Registry Editor Using Registry Trick
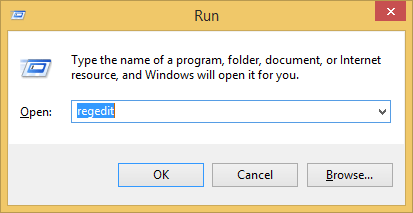
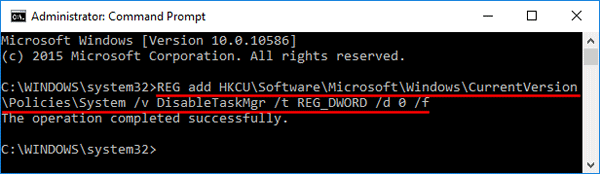
- Press the Windows key + R to bring up the Run box. Type regedit and press Enter.
- When Registry Editor opens, navigate to:
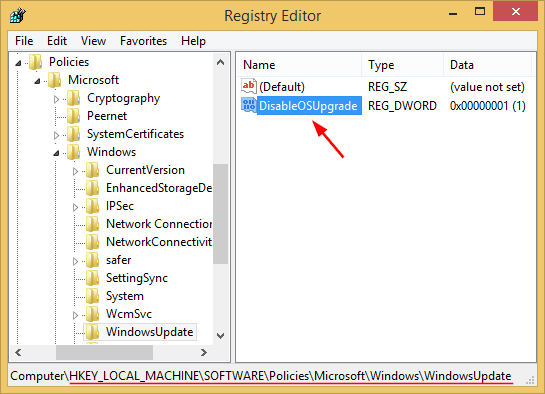
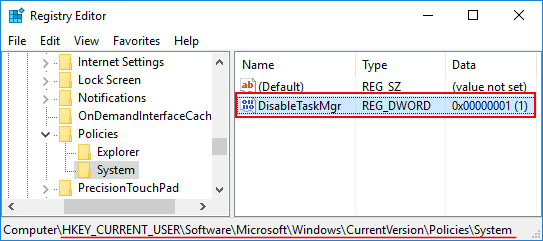
HKEY_CURRENT_USER > SOFTWARE > Microsoft > Windows > CurrentVersion > Policies > SystemIf the System key doesn’t exist, you need to create it.
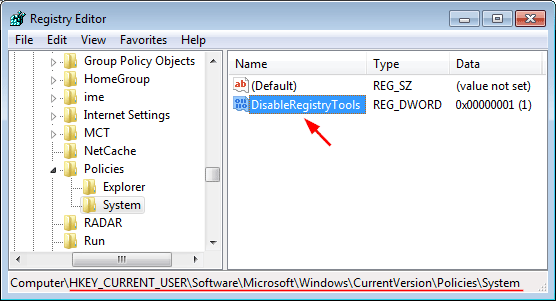
- In the right pane, right-click on any empty space and select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value. Name it DisableRegistryTools and set its value to 1.
![disable-registry-tools]()
- When you try to access Registry Editor, you’ll also get the same error message “Registry editing has been disabled by your administrator“.
This method will prevent your current user from accessing Registry Editor. To regain access, you have to log on as another administrator account and delete the registry value DisableRegistryTools.
Method 3: Disable Registry Editor Using Third Party Software
Using Protect My Folders you can lock & protect Registry Editor with a password. Anyone can’t access Registry Editor without knowing your password.
- Download and install Protect My Folders program on your computer. The first time you launch this program it will prompt your to set a password. Don’t forgot it as you’ll need it next time you run it.
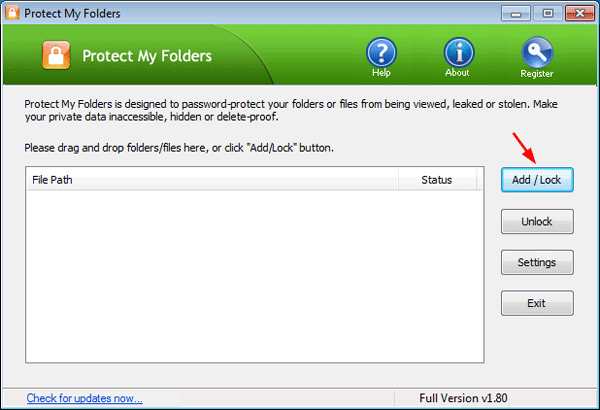
- When Protect My Folders starts, click on Add/Lock button.
![protect-my-folders]()
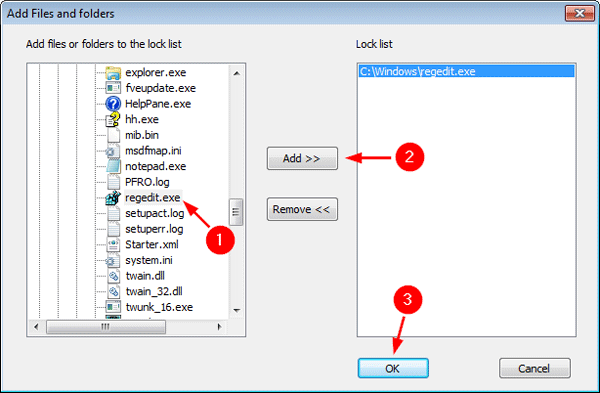
- The File/Folder selection dialog should open, choose the C:\Windows\regedit.exe file and click Add, next click OK.
![select-regedit]()
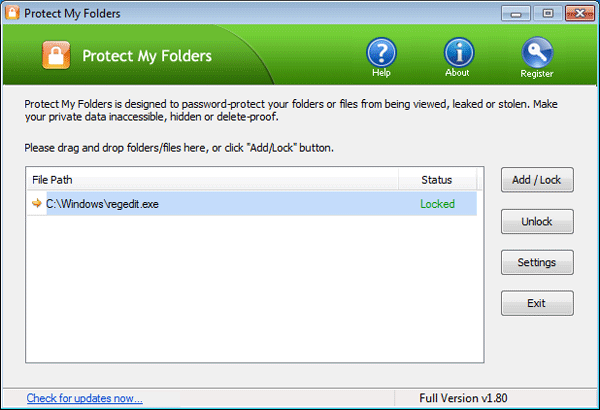
- Now you’ll see the regedit application is locked. Close Protect My Folders program.
![lock-registry-editor]()
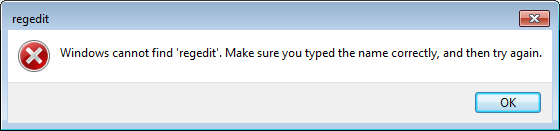
- When you try to access Registry Editor, you’ll receive the following error message:
![cannot-find-regedit]()
This method will block all users from accessing Registry Editor. To regain access you have to relaunch Protect My Folders, enter your password and unlock the regedit.exe app.